How Should A Child With Systemic Sclerosis Be Treated?
A team effort is typically needed to provide the best care for a child with systemic sclerosis.
Specialists typically involved with treating and managing a child with systemic sclerosis include the pediatric rheumatologist, who is usually the coordinator of a team that includes:
- Pediatric Cardiology
- Pediatric Pulmonology
- Pediatric Gastroenterology
- Pediatric Physical Therapy
- Occupational Therapy
Additional Providers
Dermatologists, pediatric or adult, can be helpful in co-managing some of the skin manifestations including telangiectasias and dyspigmentation.
Plastic surgeons may be helpful in calcinosis disease management, and in more severe cases when stem cell transplant is needed, pediatric bone marrow transplant and cellular therapies specialists are typically involved.
Medical Management and Treatment
Pediatric systemic sclerosis (SSc) cases are managed similar to adults with a global focus and organ specific treatments. One of the main differences is the use of corticosteroids (prednisone, I methylprednisolone) is more liberalized in juvenile onset systemic sclerosis for two reasons: 1) more common myositis and arthritis which is very responsive to corticosteroids and 2) low inherent risk of scleroderma renal crisis (<5% all cohorts studies, 0% in recent international cohort), therefore not as high of a concern for induction of SRC from corticosteroid use in children as in adults.
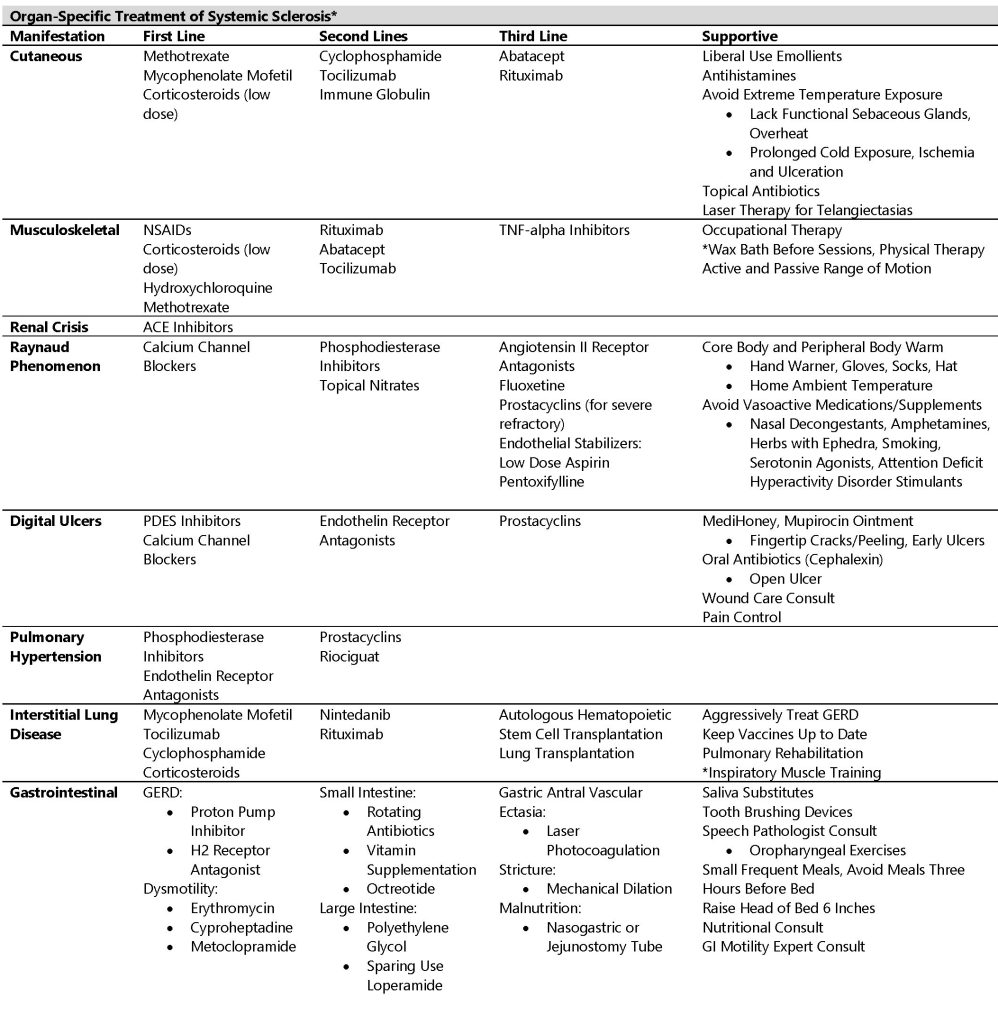
*Medications listed by evidence first to third tier. Supportive care includes author’s recommendations, Kathryn Seraphin Torok, MD, UPMC Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh.